Use of RFID in Managing Cold Chain Inventory
In this fast-paced and highly regulated supply chain environment today, accurate tracks of perishable goods are no longer a luxury- they are as critical as ever. Even a slight lapse in temperature control will cause heavy product loss, legal problems, and tarnished brand image to firms in the food, pharma, and biomedical industries.
Here is where Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology comes as a knight in shining armour in cold chain inventory management. With the availability of real-time visibility, temperature monitoring, and automation, inventory tracking RFID ensures that perishables are handled with the precision required of them.
- Understanding the RFID in the Context of Cold Chain
RFID is a wireless device-human system that identifies and tracks tags in objects through the use of electromagnetic fields. Unlike barcodes, RFID does not need a straight-line-of-sight and can scan several items simultaneously, making it fit for high-volume volume fast-moving cold chain environments.
RFID tags can be loaded with temperature sensors or linked with data loggers that transmit essential data during transit and storage in cold chain inventory systems. This continuous data flow will guarantee that the integrity of temperature-sensitive goods from point of origin to delivery is once again being maintained, therefore allowing businesses to meet the standards of safety and avoid spoilage.
Read Also: How to Fix a Refrigerator Door That Won’t Close Properly
- Real-Time Monitoring System to Prevent Product Loss
One of the greatest RFID features in the cold chain inventory is that it can monitor conditions in real time. RFID-enabled temperature sensors monitor variables including humidity and internal container temperature in real time. Automated alerts to breach of thresholds may also be generated and sent to logistics managers through an integrated system.
This proactive mindset enables businesses to detect a product before it is damaged. For example, suppose the temperature of the refrigerated truck is at unsafe levels for dairy products. In that case, the system can reach relevant staff immediately, who could reroute or fix a faulty truck. This early warning system significantly cuts the risks of spoilage and improves bottom line, and it follows compliance measures such as the FDA’s FSMA or EU Good Distribution Practice (GDP).
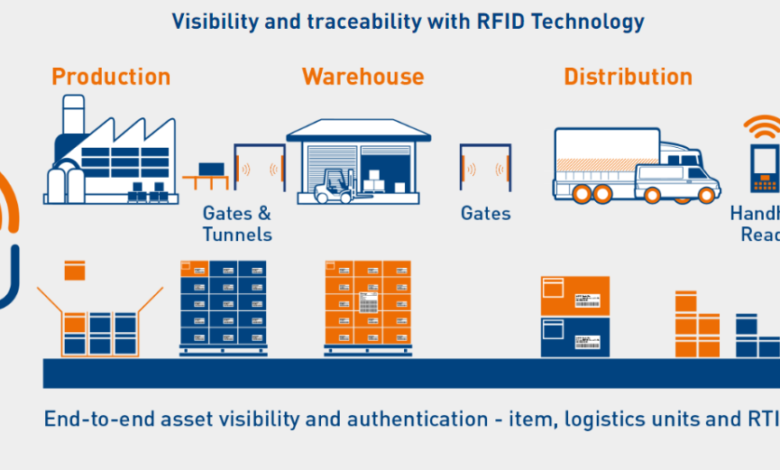
- Higher Visibility in the Supply Chain System
Using RFID, the entire journey of a perishable item is traceable. Each RFID tag has a distinct ID, corresponding to the described item’s data profile, including such information as origin, batch number, expiration date, storage conditions, and so on. When an item is transferred from the warehouse to the transporter to the retailer, a checkpoint updates data tagged to the item in real time.
Such improved traceability is immensely useful not only to internal audits but also to regulatory and recall preparedness. Suppose a consignment of frozen meat or vaccines has been exposed to the wrong temperatures. In that case, RFID solution for retail logs helps businesses identify the problem swiftly and respond with recall by batches, or firm recalls, saving both money and reputation.
Thus, the introduction of RFID into the system allows a cold storage operator to track the items properly and also to maintain the product quality and supply standardized products to the retail outlets.